Mastering Your First Ride: A Beginner’s Guide to Electric Bikes
NOV 06, 2024
Are you ready to experience the thrill of riding an electric bike (eBike)? Whether you’re an experienced cyclist or a complete beginner, getting started with an eBike is easy and fun. In this guide, we'll walk you through everything you need to know to ride your eBike safely and confidently.
1. Understand Your eBike Components
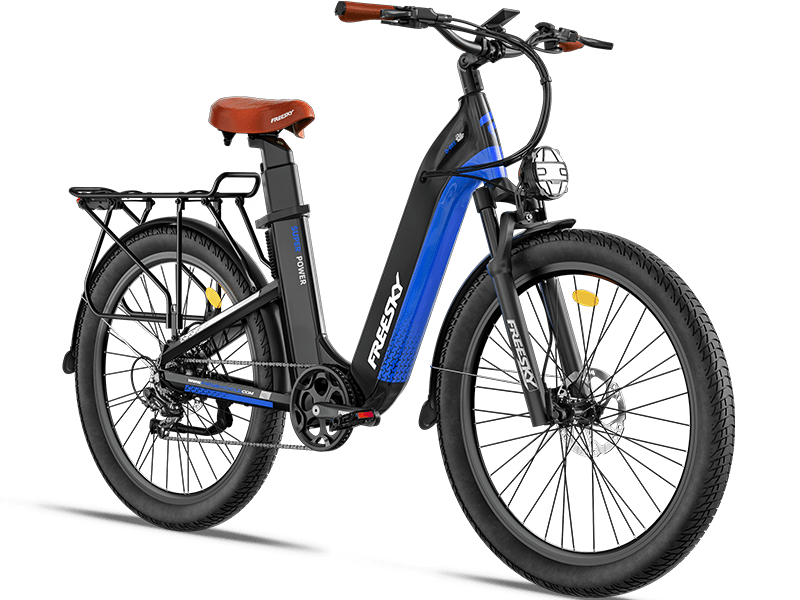
Before hitting the road, it's essential to get familiar with the main components of your eBike:
- Battery: Provides the power for your eBike to move. It’s typically located on the frame or rear rack.
- Motor: The heart of your eBike, it helps you pedal with less effort by providing an extra boost. Motors are usually located in the rear wheel hub, mid-drive system, or front wheel hub.
- Pedal Assist System (PAS): Allows you to control how much assistance you get from the motor as you pedal. You can usually adjust the level of assist via the bike’s display or control panel.
- Throttle (if applicable): Some eBikes come with a throttle that allows you to accelerate without pedaling. The throttle is typically located on the right handlebar.
- Brakes: Like any bike, eBikes come equipped with brakes. Learn how your eBike's brakes work before setting off, especially if you’re new to cycling.
- Display: Your eBike will likely have a display screen that shows battery life, speed, distance traveled, and other important data.
2. Get Comfortable with the Basics
Before taking your eBike on a long ride, it’s important to get used to its power and handling. Here’s what you should do:
- Check the battery: Ensure the battery is fully charged before you head out.
- Adjust the seat: Make sure your seat height is comfortable, with a slight bend in your knees when your foot is at the lowest point of the pedal stroke.
- Check tire pressure: Proper tire pressure is essential for safe and smooth riding.
3. Start with Low Pedal Assist
When you’re just starting, it’s a good idea to use a lower level of pedal assist to get a feel for the bike. This allows you to pedal normally and get accustomed to the extra boost from the motor.
4. Use the Throttle (If Available)
If your eBike has a throttle, start by gently twisting the throttle to accelerate. Practice using it in a controlled environment (like a parking lot or quiet street) before using it in traffic. Be sure to go easy on the throttle until you feel comfortable with the bike’s speed.
5. Practice Braking
Take some time to practice braking smoothly. Your eBike’s motor can help slow you down, but you’ll still need to use the brake levers. Apply the brakes gradually and avoid sudden, sharp braking to prevent accidents.
- Front brake: Use the front brake gently, especially when riding at higher speeds, to avoid tipping forward.
- Rear brake: Use the rear brake in combination with the front brake for more control.
6. Ride in Different Environments
Once you feel comfortable with your eBike in a controlled setting, it’s time to test it in different environments:
- Flat Roads: Practice on flat, smooth roads to get a feel for your bike’s speed and handling.
- Hills: Your eBike is great for tackling hills. Use a higher level of pedal assist to help you power up inclines. Remember, the motor will do most of the work, but you’ll still need to pedal.
- Downhill: On downhill sections, you can let the motor assist you with braking, but be cautious and always keep both hands on the handlebars.
7. Stay Safe
- Wear a helmet: Safety should always come first. Make sure you wear a helmet that fits properly.
- Follow the rules of the road: eBikes are subject to the same rules as regular bicycles. Be mindful of traffic laws and signals, especially if you’re riding in busy areas.
- Stay visible: Wear bright clothing, use bike lights, and signal when turning to make yourself visible to others.
8. Get the Most Out of Your eBike
As you become more confident on your eBike, here are a few tips to maximize your experience:
- Manage your battery: Keep an eye on the battery level, especially on longer rides. If you’re running low, switch to a lower pedal assist setting to conserve energy.
- Maintain your eBike: Regular maintenance, including tire checks, brake inspections, and battery care, will ensure your eBike runs smoothly for years to come.
Conclusion
Riding an electric bike for the first time can be exhilarating and rewarding. With the right knowledge and a little practice, you’ll be cruising around like a pro. Whether you're commuting to work, exploring new places, or simply enjoying a fun ride, eBikes offer a unique and eco-friendly way to travel.
So, get out there, start pedaling, and enjoy the ride!